# IO 流
主要由 4 个抽象类基类中派送出来。
- InputStream/Reader:所有输入流的基类。
- OutputStream/writer:所有输出流的基类。
两种区别就是前者是字节,后者是字符。
# 常见 IO 流问答
- 字节流和字符流哪个好?
答:字节流,IO 操作一般是直接操作磁盘文件,这些流在传输时都是以字节方式传递。
但是在内存中的 IO 操作就更佳适合字符流,字符流拥有缓冲区,性能更佳。
- 缓冲区的作用?
缓冲区用于需要频繁操作的场景。就是一块划分出来的特殊内存区。对于提高 IO 操作的性能有不错的作用。
- 字符流和字节流有什么区别?
还是上面的第一个问题变版,一个有缓冲区,一个没有缓冲区。
# IO 设计模式
# 装饰器模式
可用于在不改变原有对象的情况下拓展功能,有点像插件。
装饰器的核心就是 FilterInputStream(对应输入流)和 FilterOutputStream(对应输出流)。相对地对应着 InputStream 和 OutputStream 子类对象的功能。
# 适配器模式
应用在接口互不兼容的类的协调工作,联想电源适配器?
适配器和装饰器两者有何区别?
装饰器侧重动态增强原始类的功能,且支持嵌套。
适配器侧重兼容,将不兼容的接口类整合。
# 工厂模式
NIO 中主要使用了工厂模式,工厂模式是用来创建对象的。(NIO 接下来会提到)
# 观察者模式
NIO 中的文件目录监听服务用到了观察者模式。主要注意两个接口:WatchService 和 Watchable。这两个中前者是观察者,后者是被观察者。
主要的三种监听事件:
- 文件创建
- 文件删除
- 文件修改
有哪些常见的 IO 模型?
UNIX 系统下,总共有五种:
- 同步阻塞 I/O
- 同步非阻塞 I/O
- I/O 多路复用
- 信号驱动 I/O
- 异步 I/O
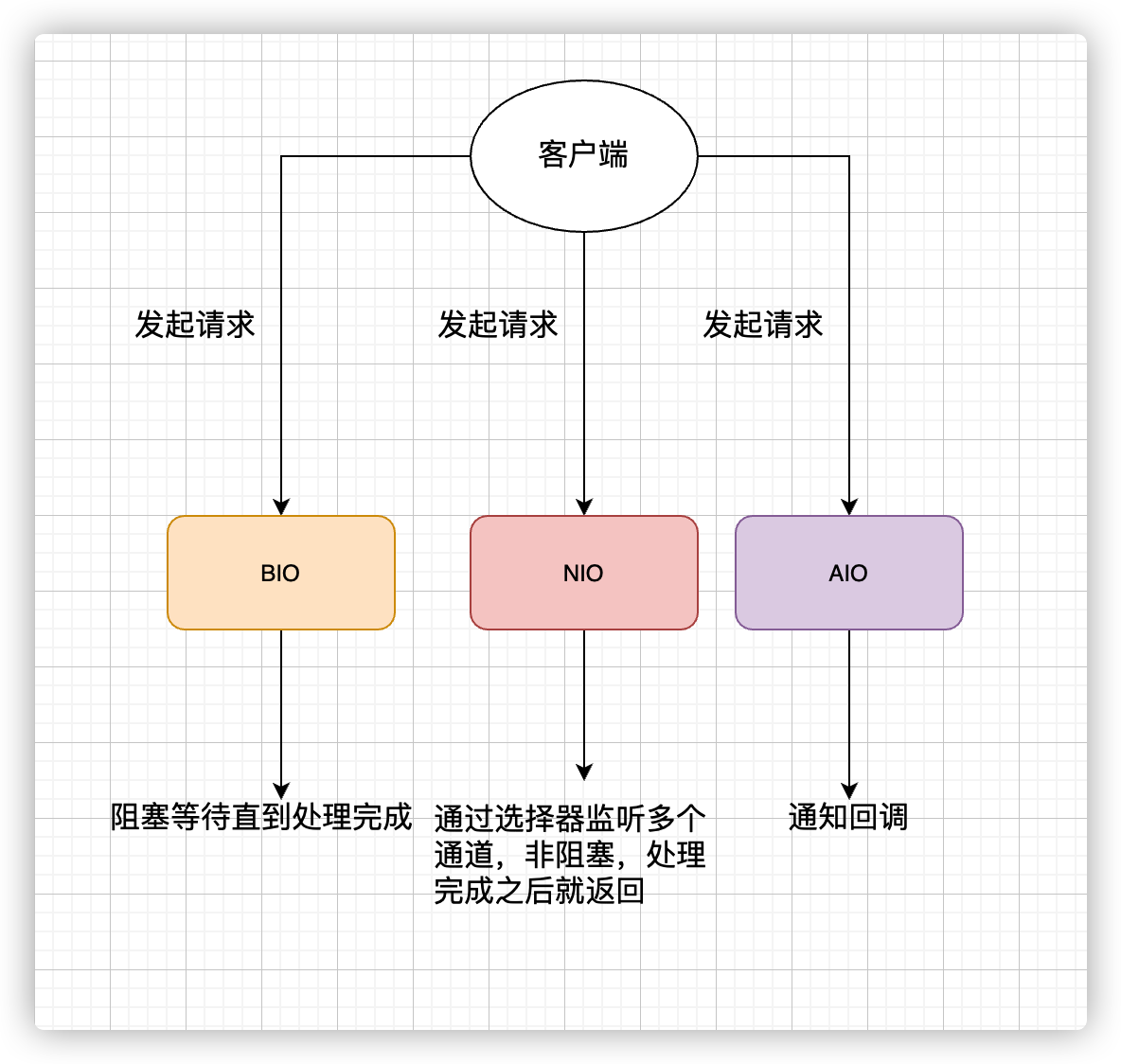
Java 中三种常见的 IO 模型
- 同步阻塞 IO 模型(Blocking I/O)
特点:应用程序 read 时,一直阻塞,直到拷贝完成。
缺点:无法应对高并发,当在十万或百万级别连接时,传统 BIO 就 g 了。
- 同步非阻塞 I/O(Non-blocking/New I/O)
特点:在 read 时不阻塞,只在拷贝时阻塞。
缺点:占用 CPU 资源较多
优化:I/O 多路复用模型,使用 Selector 选择器进行 read 前质询,待内核把数据准备好后再 read。此优化可以通过减少无效系统调用,来减少对 CPU 的消耗。
有同步当然也有异步啦。
AIO(Asynchronous I/O)
异步 IO 是基于事件和回调机制实现的,也就是应用操作之后会直接返回,不会堵塞在那里,当后台处理完成,操作系统会通知相应的线程进行后续的操作。
一张图总结三种IO
# NIO
# Channel 简述
File 读操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| package com.jun.channel;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class FileChannelDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("d:\\JAVAIdeaProjects\\Java_nio\\nio_test\\FileData\\01.txt","rw");
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int bytesRead = channel.read(buffer);
while (bytesRead != -1) {
System.out.println("读取了:"+bytesRead);
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.println((char)buffer.get());
}
buffer.clear();
bytesRead = channel.read(buffer);
}
file.close();
System.out.println("读取数据结束");
}
}
|
file 写操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| package com.jun.channel;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class FileChannelDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("d:\\JAVAIdeaProjects\\Java_nio\\nio_test\\FileData\\01.txt","rw");
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
String newData = "data jun";
buffer.clear();
buffer.put(newData.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
channel.write(buffer);
}
channel.close();
}
}
|
通道间数据传输
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| package com.jun.channel;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class FileChannelDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
RandomAccessFile aFile = new RandomAccessFile("d:\\JAVAIdeaProjects\\Java_nio\\nio_test\\FileData\\01.txt", "rw");
FileChannel fromChannel = aFile.getChannel();
RandomAccessFile bFile = new RandomAccessFile("d:\\JAVAIdeaProjects\\Java_nio\\nio_test\\FileData\\02.txt", "rw");
FileChannel toChannel = bFile.getChannel();
long position = 0;
long size = fromChannel.size();
toChannel.transferFrom(fromChannel,position,size);
aFile.close();
bFile.close();
System.out.println("传输结束!");
}
}
|
# Socket 通道
ServerSocketChannel 一个 socket 监听器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| package com.jun.channel;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class ServerSocketChannelDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port = 8888;
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello abc".getBytes());
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
while (true) {
System.out.println("等待传输数据中。。");
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if (socketChannel == null) {
System.out.println("null");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} else {
System.out.println("Incoming connection from:"+ socketChannel.socket().getRemoteSocketAddress());
buffer.rewind();
socketChannel.write(buffer);
socketChannel.close();
}
}
}
}
|
# Buffer
buffer 的几个方法
put ():将一个元素添加到缓冲区的末尾。
get ():从缓冲区的开头移除并返回一个元素。
full ():如果缓冲区已满,则返回 True,否则返回 False。
empty ():如果缓冲区为空,则返回 True,否则返回 False。
clear ():从缓冲区中移除所有元素。
size ():返回缓冲区中当前元素的数量。
peek ():返回缓冲区的下一个元素,但不删除它。
缓冲区操作:
写入缓冲区:将数据写入缓冲区,可以通过系统调用或者库函数实现。
读取缓冲区:从缓冲区中读取数据,可以通过系统调用或者库函数实现。
清空缓冲区:将缓冲区中的数据清空,可以使用库函数或者操作系统提供的清空缓冲区方法。
刷新缓冲区:将缓冲区的内容刷新到文件或者设备中,可以使用库函数或者操作系统提供的刷新缓冲区方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| package com.jun.buffer;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class BufferDemo3 {
static private final int start = 0;
static private final int size = 1024;
@Test
public void b04() throws Exception {
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("D:\\JAVAIdeaProjects\\Java_nio\\nio_test\\FileData\\01.txt", "rw");
FileChannel fileChannel = file.getChannel();
MappedByteBuffer map = fileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, start, size);
map.put(0,(byte) 97);
map.put(1023,(byte) 122);
file.close();
}
}
|
# 客户端模拟
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
| package com.jun.selector;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class SelectorDemo2 {
@Test
public void serverDemo() throws Exception {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer serverByteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",9090));
Selector selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (selector.select() > 0) {
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> selectionKeysIterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (selectionKeysIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey next = selectionKeysIterator.next();
if (next.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel nextOperate = serverSocketChannel.accept();
nextOperate.configureBlocking(false);
nextOperate.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if (next.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) next.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int length = 0;
while ((length = channel.read(byteBuffer)) > 0) {
byteBuffer.flip();
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array(),0,length));
byteBuffer.clear();
}
}
System.out.println(next);
selectionKeysIterator.remove();
}
}
}
@Test
public void clientDemo() throws Exception {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",9090));
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
byteBuffer.put(new Date().toString().getBytes());
byteBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
}
}
|
# JAVA NIO(Selector)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| package com.jun.selector;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class SelectorDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999));
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
} else if (key.isConnectable()) {
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
} else if (key.isWritable()) {
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
|
# FileLock
文件锁
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| package com.jun.filelock;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.FileLock;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
public class FileLockDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String input = "jun";
System.out.println("input:"+input);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(input.getBytes());
String filePath = "D:\\JAVAIdeaProjects\\Java_nio\\nio_test\\FileData\\01.txt";
Path path = Paths.get(filePath);
FileChannel channel = FileChannel.open(
path,
StandardOpenOption.WRITE,
StandardOpenOption.APPEND);
channel.position(channel.size()-1);
FileLock lock = channel.lock();
System.out.println("是否为共享锁:"+lock.isShared());
channel.write(buffer);
channel.close();
readFile(filePath);
}
private static void readFile(String filePath) throws Exception {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
String readLine = bufferedReader.readLine();
System.out.println("读取出内容:");
while (readLine != null) {
System.out.println(" "+readLine);
readLine = bufferedReader.readLine();
}
fileReader.close();
bufferedReader.close();
}
}
|
# 异步 FileChannel
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| package com.jun.asyncfilechannel;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousFileChannel;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class AsyncFileChannelDemo {
@Test
public void readAsyncFileChannelFuture() throws Exception {
Path path = Paths.get("D:\\JAVAIdeaProjects\\Java_nio\\nio_test\\FileData\\03.txt");
AsynchronousFileChannel fileChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(path, StandardOpenOption.READ);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Future<Integer> future = fileChannel.read(buffer, 0);
while (!future.isDone()) ;
buffer.flip();
byte[] data = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(data);
String string = new String(data, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(string);
buffer.compact();
}
}
|
# Charset
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| package com.jun.Charset;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.nio.charset.CharacterCodingException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.SortedMap;
public class CharsetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CharacterCodingException {
Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
CharsetEncoder charsetEncoder = charset.newEncoder();
CharBuffer charBuffer = CharBuffer.allocate(1024);
charBuffer.put("jun会java");
charBuffer.flip();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = charsetEncoder.encode(charBuffer);
for (int i = 0; i < byteBuffer.limit() ;i++) {
System.out.println(byteBuffer.get());
}
byteBuffer.flip();
CharsetDecoder charsetDecoder = charset.newDecoder();
CharBuffer charBuffer1 = charsetDecoder.decode(byteBuffer);
System.out.println("解码之后的结果:");
System.out.println(charBuffer1.toString());
Charset charset1 = Charset.forName("GBK");
byteBuffer.flip();
CharBuffer charBuffer2 = charset1.decode(byteBuffer);
System.out.println(charBuffer2.toString());
SortedMap<String, Charset> map = Charset.availableCharsets();
Set<Map.Entry<String,Charset>> set = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Charset> entry:
set){
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"="+entry.getValue().toString());
}
}
}
|
# 聊天室综合案例
# 服务端编写
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
| package com.jun.server;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class ChatSever {
public void startServer() throws IOException {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8000));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("服务器已经启动成功。");
for(;;){
int readChannels = selector.select();
if (readChannels == 0) {
continue;
}
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
acceptOperator(serverSocketChannel,selector);
}
if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
readOperator(selector,selectionKey);
}
}
}
}
private void readOperator(Selector selector, SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel)selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readLength = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
String message = "";
if (readLength > 0) {
byteBuffer.flip();
message += Charset.forName("UTF-8").decode(byteBuffer);
}
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
if (message.length() > 0) {
System.out.println(message);
castOtherClient(message,selector,socketChannel);
}
}
private void castOtherClient(String message, Selector selector, SocketChannel socketChannel) throws IOException {
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeySet = selector.keys();
for (SelectionKey selectionKey: selectionKeySet){
Channel tarChannel = selectionKey.channel();
if (tarChannel instanceof SocketChannel && tarChannel != socketChannel) {
((SocketChannel)tarChannel).write(Charset.forName("UTF-8").encode(message));
}
}
}
private void acceptOperator(ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel, Selector selector) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
socketChannel.write(Charset.forName("UTF-8")
.encode("欢迎你进入聊天室,你与其它人还不是朋友,请注意隐私安全"));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new ChatSever().startServer();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
# 客户端编写
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| package com.jun.client;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ChatClient {
public void startClient(String name) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel =
SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",8000));
Selector selector = Selector.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
new Thread(new ClientThread(selector)).start();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String msg = scanner.nextLine();
if (msg.length() > 0) {
socketChannel.write(Charset.forName("UTF-8").encode(name + ":" + msg));
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
|

